HPC in Deutschland - Wer? Was? Wo?
Rechenzentrum
155.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
256 Knoten , 38.848 CPU-Kerne (AMD, Intel)
52 GPGPUs (AMD, Nvidia)
Fachgruppe Physik
78.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
281 Knoten , 17.968 CPU-Kerne (AMD, Intel)
40 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Center for Scientific Computing
19.340 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 55.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
110 Knoten , 7.040 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
880 GPGPUs (AMD)
Deutscher Wetterdienst

16.578 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 319.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
645 Knoten , 54.400 CPU-Kerne (NEC)

12.775 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 246.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
497 Knoten , 41.920 CPU-Kerne (NEC)
Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron
37 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung)
43 Knoten , 2.416 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
14 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
2.321 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 393.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
764 Knoten , 26.668 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
282 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Deutsches Klimarechenzentrum GmbH

16.600 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 863.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
3.042 Knoten , 389.376 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
240 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
ZDV
543 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 41.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
302 Knoten , 6.120 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
124 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Competence Center High Performance Computing (CC-HPC)

67 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 14.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
198 Knoten (Unknown FDR-Infiniband) , 3.224 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
2 GPGPUs (Nvidia)

35 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 6.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
90 Knoten (Unknown FDR-Infiniband, QDR-Infiniband) , 1.584 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
3 GPGPUs (Nvidia) , 2 Many-Core-Prozessoren (Intel)
Gesellschaft für wissenschaftliche Datenverarbeitung mbH Göttingen

2.883 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 90.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
402 Knoten (Unknown QDR-Infiniband, FDR-Infiniband, Intel Omnipath, FDR-Infiniband) , 16.640 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
278 GPGPUs (Nvidia) , 302 Anwendungen (454 Versionen)

8.261 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 487.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
1.473 Knoten (Intel Omnipath) , 116.152 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
12 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
14.760 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 74.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
126 Knoten , 8.632 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
504 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Zentrum für Informations- und Medientechnologie
64.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
212 Knoten , 6.820 CPU-Kerne (AMD, Intel, Alpha Data)
230 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Zentralabteilung Informationsdienste und Computing
6.800 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 255.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
357 Knoten , 29.776 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
268 GPGPUs (Nvidia) , 2 FPGAs (AMD XILINX)
hessian.AI
8.830 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 159.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
81 Knoten , 2.784 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
632 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Hochschulrechenzentrum

8.500 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 553.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
1.231 Knoten ( HDR100-Infiniband, Mellanox HDR100-Infiniband) , 123.072 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
100 GPGPUs (Nvidia, Intel, AMD)
Höchstleistungsrechenzentrum Stuttgart

120.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
476 Knoten , 14.480 CPU-Kerne (Intel, NEC)
16 GPGPUs (AMD, Nvidia)
48.100 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 286.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
444 Knoten , 34.432 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
752 GPGPUs (AMD)
IT Center der RWTH Aachen University

11.484 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 226.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
684 Knoten , 65.664 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
208 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Jülich Supercomputing Centre (JSC)

85.000 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 749.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
3.515 Knoten (Mellanox EDR-Infiniband, HDR200-Infiniband) , 168.208 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
3956 GPGPUs (Nvidia)

18.520 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 444.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
780 Knoten (Mellanox HDR100-Infiniband) , 99.840 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
768 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
930.000 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 703.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
6.000 Knoten , 1.728.000 CPU-Kerne (Nvidia)
24000 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Zuse-Institut Berlin

10.707 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 677.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
1.192 Knoten (Intel Omnipath, NDR-Infiniband) , 113.424 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
42 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Leibniz-Rechenzentrum der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften

54.860 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 822.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
6.720 Knoten (Intel Omnipath, Mellanox HDR200-Infiniband) , 337.920 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
960 GPGPUs (Intel)
Max Planck Computing & Data Facility

24.800 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 517.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
1.784 Knoten , 128.448 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
768 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
4.900 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 445.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
768 Knoten , 98.304 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
36.000 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 75.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
300 Knoten , 14.400 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
600 GPGPUs (AMD)
Paderborn Center for Parallel Computing

835 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 51.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
274 Knoten (Intel Omnipath) , 10.960 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
18 GPGPUs (Nvidia)

7.100 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 347.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
1.121 Knoten (Mellanox HDR100-Infiniband) , 143.488 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
136 GPGPUs (Nvidia) , 80 FPGAs (Bittware, AMD XILINX)
18.900 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 593.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
743 Knoten (Mellanox NDR-Infiniband) , 142.656 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
108 GPGPUs (Nvidia) , 32 FPGAs (AMD XILINX)
Regionales Hochschulrechenzentrum Kaiserslautern-Landau (RHRZ)

3.072 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 52.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
489 Knoten (Unknown QDR-Infiniband, Intel Omnipath) , 10.520 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
56 GPGPUs (Nvidia) , 56 Anwendungen (228 Versionen)
489 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 68.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
244 Knoten ( Omnipath) , 4.240 CPU-Kerne (AMD, Intel)
56 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Hochschulrechenzentrum
304.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
277 Knoten , 28.384 CPU-Kerne (AMD, Intel)
320 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
IT.SERVICES
URZ
Scientific Computing Center

27.960 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 291.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
799 Knoten ( HDR200-Infiniband) , 60.460 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
756 GPGPUs (Nvidia)

8.865 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 127.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
393 Knoten (Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) NDR-Infiniband, HDR200-Infiniband) , 27.632 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
188 GPGPUs (Nvidia, AMD)
Scientific Computing Center
IT und Medien Centrum
Universität Bielefeld – Fakultät Physik
Zentrum für Informations- und Mediendienste
5.500 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 177.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
259 Knoten , 29.008 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
68 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Regionales Rechenzentrum (RRZ)
2.640 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 147.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
182 Knoten , 34.432 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
32 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Zentrum für Informations- und Medientechnologie
119.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
459 Knoten , 29.376 CPU-Kerne (Intel, AMD)
20 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Kommunikations- und Informationszentrum (kiz)
188.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
692 Knoten , 33.216 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
28 GPGPUs (Nvidia) , 2 FPGAs (Bittware)
Zentrum für Informationsverarbeitung
Zentrum für Datenverarbeitung
3.125 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 190.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
1.948 Knoten (Intel Omnipath) , 52.248 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
188 GPGPUs (Nvidia, NEC)
2.800 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 219.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
600 Knoten ( HDR100-Infiniband) , 76.800 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
40 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Zentrum für Informationsdienste und Hochleistungsrechnen
5.443 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 34.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
34 Knoten ( HDR200-Infiniband) , 1.632 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
272 GPGPUs (Nvidia)

4.050 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 315.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
630 Knoten ( HDR100-Infiniband) , 65.520 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
762 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 94.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
188 Knoten ( HDR200-Infiniband) , 24.064 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
39.664 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 111.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
148 Knoten ( HDR200-Infiniband) , 9.472 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
592 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
Zentrum für nationales Hochleistungsrechnen Erlangen (NHR@FAU)
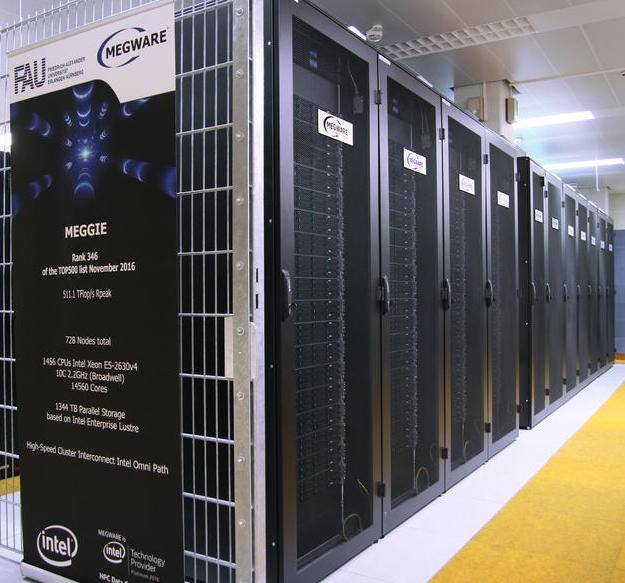

511 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 46.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
728 Knoten (Intel Omnipath) , 14.560 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
21 Anwendungen (61 Versionen)

6.080 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 78.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
82 Knoten (Mellanox HDR200-Infiniband, HDR200-Infiniband) , 10.496 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
656 GPGPUs (Nvidia)
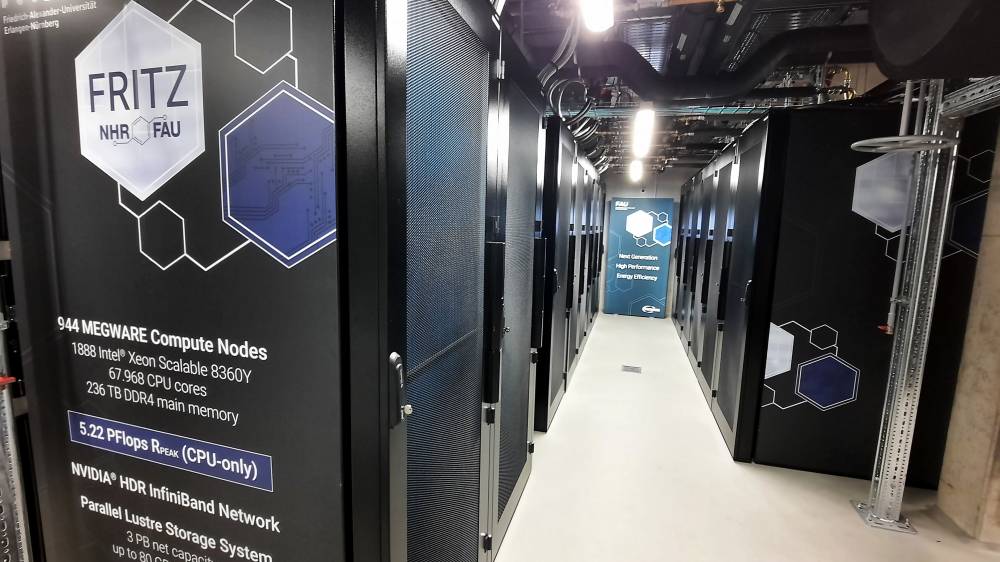

5.450 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 248.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
992 Knoten (Mellanox HDR100-Infiniband) , 71.424 CPU-Kerne (Intel)
51.920 TFlop/s (Gesamtleistung) , 144.00 TiB (Hauptspeicher)
192 Knoten , 24.576 CPU-Kerne (AMD)
768 GPGPUs (Nvidia)